Have you ever asked yourself how you can increase conversions or improve your search engine rankings? It’s well known that Google and other search engines are influenced in their analysis by your website loading speed, and there are also various e-commerce studies that directly correlate a slow website with few sales.
There are a few solutions for improving your website speed:
-
- Minification and concatenation of your website css and js files;
- Compressing your website images;
- Using specific webservers for your website workload (eg: Nginx and Lighttpd);
- Implementing a caching system (using Varnish or Nginx).
At ClusterCS, we have always focused on automation, flexibility and ease of use.
One great solution for implementing improvements for points 3 and 4 is to implement an HAProxy load balancer that redirects and manages the traffic and caching system while also allowing you to apply improved security rules for your website.
This is usually done editing the HAProxy config but a lot of times it becomes more difficult when you are trying to test various rules quickly and restrict them to a few initial visitors.
ClusterCS’s Speed engine is a traffic router for the web services that can deliver your website content. The Speed section interface offers an intuitive rule builder for sending and resolving web requests with the desired web service based on various conditions. The same logic applies to single servers and complex server clusters managed by ClusterCS. For more information on the ClusterCS Speed engine concepts please read the ClusterCS Speed Engine – Concepts section.
The Speed engine functionality is available for setups that utilize the HAProxy service as the web domain entry point. Services that can be utilized for traffic routing include Apache, NGINX, Lighttpd and Varnish, given that their settings have enabled HAproxy as the upper layer 7 load balancer. The default “Smart LAMP” setup provides this entire functionality out of the box.
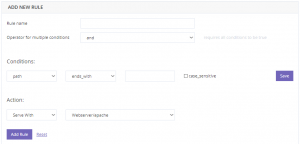
A speed rule is composed of conditions and associated action. If the conditions are met for a request, the selected action is performed. It is very important to remember that the order of the rules matters. If a certain rule meets the criteria, its action will be executed, and remaining rules will no longer be evaluated.
If none of the rules match the received request, it will be forwarded to the web service assigned as default in Speed.
Since examples are easy to understand in this case, let’s go over a few scenarios.
The first step you need to take is to create a new rule-set that suits your needs.
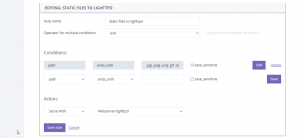
Serve static files with Lighttpd
This rule states that if the path component of the URL ends with common static file extensions, the rule should be handled by Lighttpd. It is a default rule added by ClusterCS when adding a new domain to instantly improve the server resource usage from your web site requests.
Sometimes your website script may not provide the resource at the exact URL location (for eg: on-the-fly generated thumbnails in Drupal) which can lead to Lighttpd returning a 404 Not Found error. In such cases you may disable or remove this rule so that traffic flows to your default backend service or to another rule that you create to better handle the situation.
Since these resources can be generated on-the-fly by the script you can often find great improvements replacing the static files rule with a “Cache With” rule to intercept this traffic. This alleviates the problem of the script continuously generating resources on every request. For more information on “Cache With” action please read the following KB article < Cache with >.
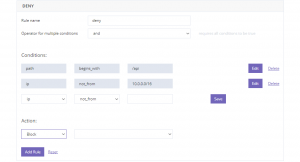
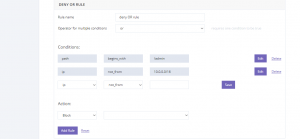
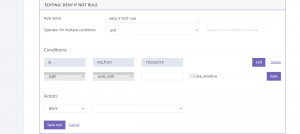
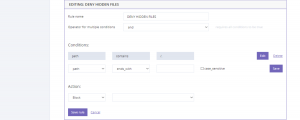
Deny traffic
This rule states that if the path component of the URL begins from a specific /path and the IP is from the mentioned subnet, all the incoming traffic from that subnet will be automatically blocked.
Similar scenarios can be made for when the path component of the URL ends with a specific /path
Securing the traffic outside your physical work location can also be a useful security maneuver to keep malicious intends outside your domain.
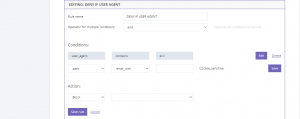
Denying based on User Agent is possible as well, if the user agent contains a specific defined syntax, all its traffic will be blocked.
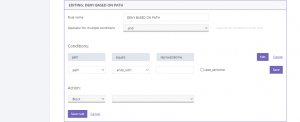
Path-based traffic denial is done based on the source of the files on the domain, in the given example, if the path is trying to be accessed directly via the link, the traffic will be blocked. This gives your domain extra security for particular sensitive files and data.
Having your hidden files being unable to be accessed is really important especially when you’re holding hidden configuration files.
Redirect Rules
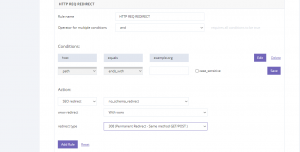
HTTP REQ Redirect
In the given example the host which is your domain will be redirected to the www. version of the site permanently when accessing the site via the non-www link.
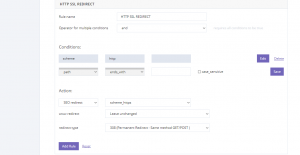
HTTP SSL Redirect
The traffic on your site will be forced into being served permanently with HTTPS regardless of the www/non-www version. We are using 308 as the redirect rule in order to preserve the request type and not break any forms that might point to non-https versions.
Caching
Caching is great improvement for your web site speed. In most cases it achieves instant visible speed gains and great advantages in SEO rankings. ClusterCS offers two caching engines: Varnish and NGINX allowing you to pick what best fits your project requirements. If you need help deciding on an implementation send us a message. Same automation features have been implemented for both systems, so you can obtain quick advantages with a few clicks for many scenarios.
You can have multiple “Cache With” rules for a domain and you can customize the settings for each zone individually.
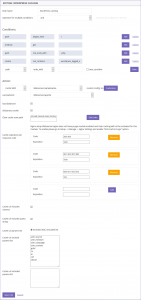
Here’s an example WordPress caching rule. For more information please read the following KB article on < Caching on WordPress using nginx >
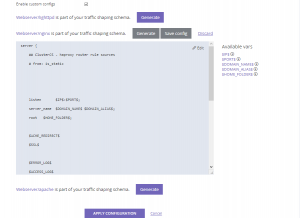
Custom configs
ClusterCS allows for custom traffic shaping schemas for advanced users. Once the custom config is generated you can modify the configuration file directly in your browser. It contains a series of placeholders marked with a starting and ending $ sign which are later replaced by ClusterCS according to your configuration and speed rules. We advise against replacing or removing those as in most cases it will result in broken configurations. These elements should not interfere with any customization you need.
Website performance optimization isn’t easy, but for sure it becomes way easier when you have the right tools. What other performance tips are you using on your own websites ? Let us know in the comments below.